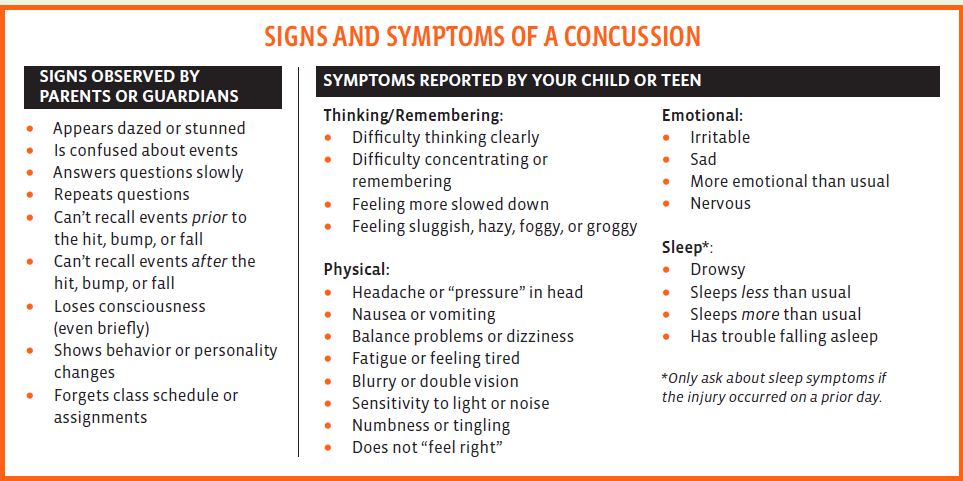
What Should You Do if Your Teen or Child Has a Possible Concussion?
A study published online in JAMA Neurology in February 2021 found that over five seasons, 72% of concussions and 67% of head impact exposure occurred in practice, not gameplay. As a parent, you should be aware of the signs and symptoms of a concussion as well as what your next steps should be during recovery.
As a parent, if you think your child or teen may have a concussion, you should:
- Remove your child or teen from play.
- Keep your child or teen out of play the day of the injury. Your child or teen should be seen by a health care provider and only return to play with permission from a health care provider who is experienced in evaluating for concussion.
- Ask your child’s or teen’s health care provider for written instructions on helping your child or teen return to school. You can give the instructions to your child’s or teen’s school nurse and teacher(s) and return-to-play instructions to the coach and/or athletic trainer.
DO NOT try to judge the severity of the injury yourself. Only a health care provider should assess a child or teen for a possible concussion. Concussion signs and symptoms often show up soon after the injury. But you may not know how serious the concussion is at first, and some symptoms may not show up for hours or days. The brain needs time to heal after a concussion. A child’s or teen’s return to school and sports should be a gradual process that is carefully managed and monitored by a health care provider.
How Can I Keep My Teen or Child Safe?
Sports are a great way for children and teens to stay healthy and can help them do well in school. To help lower your children’s or teens’ chances of getting a concussion or other serious brain injury, you should:
Help create a culture of safety for the team.
- Work with their coach to teach ways to lower the chances of getting a concussion.
- Talk with your children or teens about concussions and ask if they have concerns about reporting a concussion. Talk with them about their concerns; emphasize the importance of reporting concussions and taking time to recover from one.
- Ensure that they follow their coach’s rules for safety and the rules of the sport.
- Tell your children or teens that you expect them to practice good sportsmanship at all times.
- When appropriate for the sport or activity, teach your children or teens that they must wear a helmet to lower the chances of the most serious types of brain or head injury. However, there is no “concussion-proof” helmet. So, even with a helmet, it is important for children and teens to avoid hits to the head.
In every scenario, it is important to receive an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare professional. Physical therapy can play an important role in monitoring the healing process after a concussion has occurred. As physical therapists, we are trained in the step-by-step process of monitoring the post-concussed patient and safely returning them to their previous activities. Getting diagnosed and seeking medical attention immediately is crucial to a healthy recovery. For more information about concussions visit www.cdc.gov/concussion.