For years, seniors have attributed their aches, pains, and illnesses to the normal aging process. Age is often used as a reason to avoid exercise. But a regular exercise program can improve the quality of your life and help you avoid illness, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. As always, you should consult with your health care provider before starting any exercise program.
WHAT WE KNOW
Most people know that with age, come certain physiological changes. Studies show that we lose the following as we age:
• Lean muscle tissue—Most of us will lose muscle mass as we get older. We usually hit our peak muscle mass early—around age 20—and begin losing muscle mass thereafter.
• Aerobic capacity—The aerobic capacity is the ability of the heart and the body to deliver and use oxygen efficiently. Changes in the heart and decrease in muscle tissue decrease aerobic capacity.
• Balance—As we age, our ability to balance decreases, making falls and injuries more likely. The loss of muscle is a major contributor to losses on balance.
• Flexibility—Our joints and tendons lose some of their range of motion with age, making it difficult to bend and move around comfortably.
• Bone density—Most of us reach our peak bone density around age 20. After that, bones can become gradually thinner and weaker, which can lead to osteoporosis.
Fortunately, regular exercise can help delay some of these changes and give you the energy you need to do everyday activities like walking, shopping, and playing with your grandchildren. Exercise may even help decrease depression and stress, improve mood and self-esteem, and postpone age-related cognitive decline.
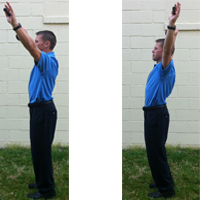
By adding endurance, strength, flexibility, and balance training into your routine, you will be healthier, happier, and more energetic.

ENDURANCE
Decades ago, doctors rarely recommended aerobic exercise for older people. But we now know that most people can safely do moderate exercises. Studies have shown that doing aerobic exercise just a few days a week can bring significant improvements in endurance.
Aim to get 30 minutes of moderate exercise—such as brisk walking, bicycling, or swimming—at least 5 days a week. You do not have to do 30 minutes at once—you can break these sessions up into two 15-minute sessions or three 10-minute sessions. Moderate exercise will cause your heart rate to rise and your breathing to be slightly elevated, but you should still be able to carry on a conversation.
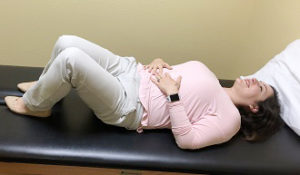
STRENGTH
It is not just aging that makes people lose muscle. One of the main reasons older people lose muscle mass is that they stop exercising and doing everyday activities that build muscle.
Building stronger muscles can help protect your joints, strengthen your bones, improve your balance, reduce the likelihood of falls, and make it easier for you to move around in general. Even small changes in your muscle size and strength—ones that you cannot even see—will make things like walking quickly across the street and getting up out of a chair easier to do.
Aim to do strength exercises (eg, weight lifting) every other day, or at least twice a week. For each exercise, do three sets of 8-12 repetitions.
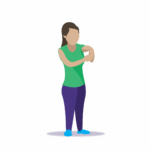
FLEXIBILITY
Increasing your overall activity level and doing stretching exercises can markedly improve your flexibility.
To improve the flexibility—or range of motion—of your joints, incorporate bending and stretching exercises into your routine. A good time to do your flexibility exercises is after your strength training routine. This is because you muscles will already be warmed up. Examples of exercises that you may enjoy include Tai chi, yoga, Pilates, and exercises that you do in the water.
By regularly stretching, you will be able to move around easier. You may also feel less stressed, and your posture will improve.
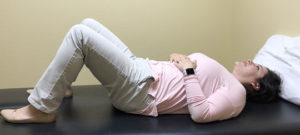
BALANCE
Just becoming more physically active will improve your balance and decrease your risk of falling. If you add some basic balancing exercises to your exercise routine, you will begin feeling more stable on your feet. Balance exercises can be done just about anywhere and usually require no more equipment than a chair.
Keep in mind that if you are having severe problems with balance, a fall prevention physical therapy program can be a great way to regain your balance, increase strength or improve flexibility.
GETTING STARTED
To avoid injury, start slowly. Add one or two sessions a week at first and progress from there as you begin to feel stronger. A physical therapist, or other health professional, can help develop a program that will be both safe and effective. Check with your local fitness or community center, which may offer exercise classes designed especially for older adults. Check with your primary health care provider if you are planning to participate in vigorous activities.
Remember, it is never too late to start exercising. The sooner you start, the sooner you will start feeling healthier, more energetic, and less stressed.
RESOURCES:
American Heart Association
http://www.heart.org
The President’s Council on Physical Fitness, Sports, and Nutrition
http://www.fitness.gov
CANADIAN RESOURCES:
Health Canada
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca
Public Health Agency of Canada
http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca
REFERENCES:
Effects of aging. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons website. Available at: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00191. Updated September 2009. Accessed April 4, 2016.
Exercise and physical activity: your everyday guide from the National Institute on Aging. National Institute on Aging website. Available at: http://www.nia.nih.gov/health/publication/exercise-physical-activity-your-everyday-guide-national-institute-aging-1. Updated February 16, 2016. Accessed April 4, 2016.
Physical activity: glossary of terms. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/physical/terms/index.htm#Moderate. Updated June 10, 2015. Accessed on April 4, 2016.
EBSCO Information Services is fully accredited by URAC. URAC is an independent, nonprofit health care accrediting organization dedicated to promoting health care quality through accreditation, certification and commendation.