Optimizing your bike and clothing isn’t just for competitive racers. Even if you’re just looking to ride a few miles recreationally, you can be more comfortable and have more fun by following our tips for a more enjoyable bike ride!
1. Check Tire Pressure
If your tires are too soft, you have a much higher chance of “pinching” a tube, causing a flat. Low pressure also increases rolling resistance, making it more difficult for you to ride at a normal speed. Check the sidewall of your tires for recommended pressure range; it doesn’t need to be at the maximum, but be sure it’s at or above the minimum.
2. Seat Angle
Everyone has a different preference on exact seat angle and position, but it should be roughly level. Deviations of 1-2 degrees up or down are OK, but don’t point up or down too much. This can place unnecessary pressure on pelvic soft tissue or the hands/wrists.
3. Seat Height
An old belief about seat height was that you must be able to touch the ground with both feet when sitting on the saddle. If you are very new to cycling, this does improve your ability to stay upright at very slow speeds. A seat that is too low, can put excess pressure on your knees and back, making it less efficient. A “proper” seat height has the knee at about 30 degrees of bend at the lowest point in the pedal stroke.
4. Stay Hydrated
Carry water with you on any ride longer than 30 minutes (shorter in hot conditions). You can use a backpack-style hydration pack, or a simple water bottle and cage. Almost all bicycles have bolts to hold a water bottle cage. Whichever method you choose, get familiar with it and get in the habit of using it often.
5. Know How to Change a Tube
Carry the items needed to replace a tube in the event of a flat tire. Your local bike shop can help you with choosing these items. These can all be carried in a bag under your seat. You don’t need to be Nascar pit-crew-fast at it, but you want to know how to fix a flat tire so you don’t end up stranded.
6. Like Lycra
Very few people think of bike shorts as a good fashion statement. However, if you’re riding more miles, especially in warm weather, they provide comfort that can’t be matched with basketball or running shorts.
7. Be Visible
Along with the bike shorts, make sure your t-shirt or jersey is a bright color that will keep you visible in traffic. If there is a chance you’ll be riding near or in darkness, be sure to have at least a rear and preferably also a front light on your bicycle.
8. Riding Shouldn’t Hurt
Sure, if you’re looking to get a hard workout or ride fast, your legs will feel the burn. However, if your body and bike are working together properly, riding shouldn’t cause any joint pain. If you can’t ride without getting neck, back, hip, or knee pain, consider having a professional look at either your body or your bike fit. Better yet, have a physical therapist who is versed in bike fitting address both at the same time. The answer to most aches and pains is rarely just in one area (bike fit or bodywork), and a combined approach will usually work best for alleviating pain and getting the most out of your ride.

Let Physical Therapy help you before your pain turns into an injury.
What an ache tells you:
• It’s the first clue your body is telling you something is wrong.
• Your body can accommodate the ache, but eventually, a breakdown will happen.
• While you accommodate to your ache, weakness, and lack of flexibility start.
• Once you have a breakdown, the pain will begin, and more than likely you will stop doing the activities you currently enjoy.
How physical therapy can help prevent sports injuries:
• Modify exercise routines when you have a minor ache and pain (This does not always mean you need to stop exercising!)
• Get assessed for weakness and flexibility issues to address biomechanical deficits.
• Educate on faulty or improper posture or body mechanics during exercise
• Educate and help with techniques on exercises that help your muscles stretch farther. Flexibility training helps prevent cramps, stiffness, and injuries, and can give you a wider range of motion.
• Correct muscle imbalances through flexibility and strength training.
• Alleviate pain.
• Correct improper movement patterns.
Common Cycling-related pain and injuries that Physical Therapy can treat:
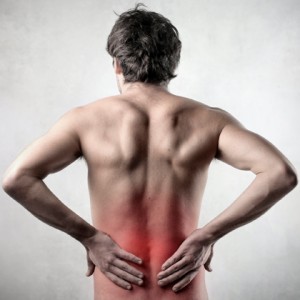
• Low Back Pain
• Neck Pain
• Foot numbness
• Shoulder pain
• Muscle strains
• Hand pain/numbness
This information about having a more enjoyable bike ride was written by Advanced Physical Therapy, a physical therapy group that uses progressive techniques and technologies to stay on the forefront in their field. Their staff is committed to providing patients with advanced healing techniques. For more information click here.
Struggling with an ache, pain, or simply need help getting your bike fitted? Our team can help make sure you get the most out of your time on your bike!