Pre Run Stretches, Why? How? When? For how long? Dynamic? Static? Ballistic?
Lately, it seems as though this simple principle has become increasingly difficult to understand. Ask a group of healthcare professionals how to stretch, and you are likely to get varying responses. This is in part due to the fact that stretching is ‘personal’. By that, we mean that each unique individual has different requirements to maximize ‘their’ benefit from stretching. This individualization of routine is largely influenced by age, health, exercise profile, and injury history. A good program will encompass both dynamic (actively moving a joint through the range of motion required for a sport) and static stretching (holding a stretch with no movement). Below, we will give an example of dynamic stretches for runners, followed by running and finishing with static stretching.
Pre-run, a good dynamic routine will incorporate sport-specific movements. The program below targets the major muscles of running. Remember to start slow with small movements, focus on form, and pick up the speed/increase the range of motion as the exercises get easier. A good dynamic warm-up lasts approximately 10 minutes:
- Leg Lifts (Swing one leg out to the side and then back across your body in front of your other leg. Repeat 10 times on each side.)
- Butt Kicks (While standing tall, walk/jog forward with an exaggerated backswing so that your heels come up towards your glutes. Repeat 10 times on each side.)
- Pike Stretch (Get in a “pike” position (hips in the air). Put your right foot behind your left ankle. With your legs straight, press the heel of the left foot down. Release. Repeat 10 times on each side.)
- Hacky-Sack (Lift your left leg up, bending the knee so it points out. Try to tap the inside of your left foot with your right hand without bending forward. Repeat 10 times on each side.)
- Toy Soldier (Keeping your back and knees straight, walk forward, lifting your legs straight out in front and flexing your toes. Advance this by adding a skipping motion. Do 10 reps on each side.)
- Walking Lunges (Step forward using a long stride, keeping the front knee over or just behind your toes. Lower your body by dropping your back knee toward the ground. Maintain an upright posture and keep your abdominal muscles tight. Repeat 10 times on each side.)
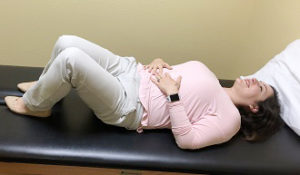
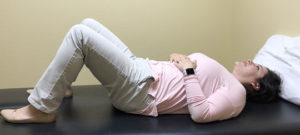
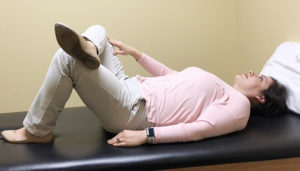
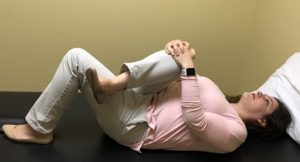
POST-RUN A good static stretching routine will target the major muscles of running including the calves, hamstrings, and hip flexors. For maximum benefit from static stretching, hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds and not more than 2 minutes. Repeat for each side of the body, and complete at least one stretch per muscle group on a consistent basis. This is just one example of a sport-specific routine that we can develop. Our professionals’ knowledge as movement scientists coupled with our understanding of the complexities of the sport, position us uniquely to design, develop, and individualize comprehensive stretching routines.
The article above provided by Plymouth Physical Therapy Specialists